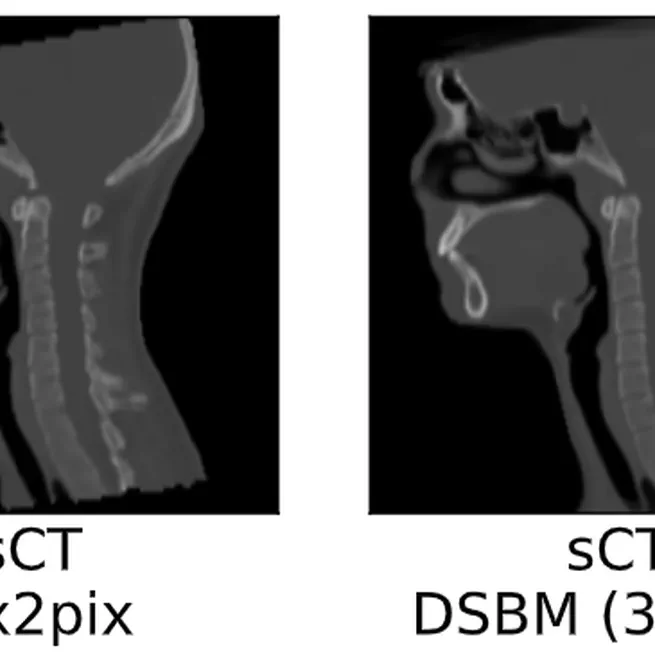
In this study, we propose the Diffusion Schrödinger Bridge Models (DSBM) which enhances the performance of MRto-CT image synthesis, both in quality and efficiency. By learning the nonlinear diffusion processes between MR and CT data distributions and initiating synthesis from a prior distribution, DSBM outperforms traditional methods, as validated in our head and neck cancer case studies. This approach has demonstrated its value through comprehensive evaluations at both the image and dosimetric levels. DSBM can improve the accuracy and efficiency of MR-based treatment planning in proton therapy, which could potentially reduce imaging-related dose and improve patient outcomes in radiotherapy.
Jul 8, 2024
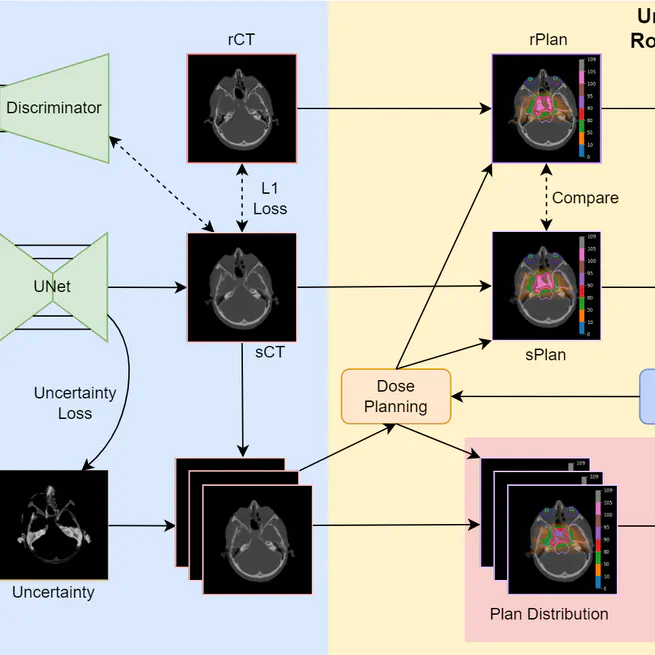
The enhanced framework incorporates 3D uncertainty prediction and generates high-quality sCTs from MR images. The framework also facilitates conditioned robust optimisation, bolstering proton plan robustness against network prediction errors. The innovative feature of uncertainty visualisation and robust analyses contribute to evaluating sCT clinical utility for individual patients.
Feb 1, 2024
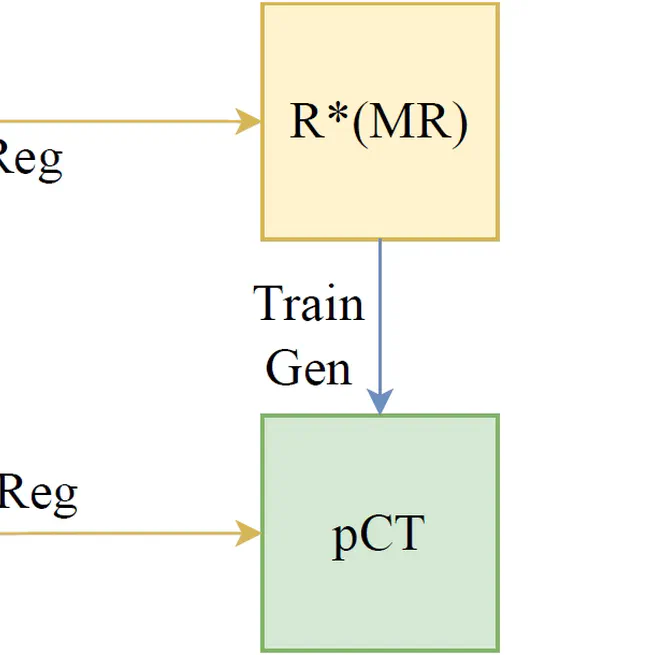
In this study, we developed an approach that substantially improves the anatomical accuracy of synthetic CT (sCT) images for MR-based radiotherapy planning. By integrating image generation with the deformable registration processes, the novel framework effectively addresses the inherent challenges in MR-CT registration and sCT evaluation. The methodological synergy of generation and registration networks, coupled with a strategic approach to proton dose planning, contributes to enhancing treatment planning accuracy. This study represents a meaningful step forward in the application of MR-based proton treatment planning and daily adaptive replanning, offering potential improvements in reducing the imaging-related dose and patient outcomes in the field of radiotherapy.
Jan 20, 2024

Uncertainty-aware MR-base CT synthesis for robust proton planning of skull-based tumour
Dec 20, 2022