Continuous sPatial-Temporal Deformable Image Registration (CPT-DIR) for motion modelling in radiotherapy: beyond classic voxel-based methods
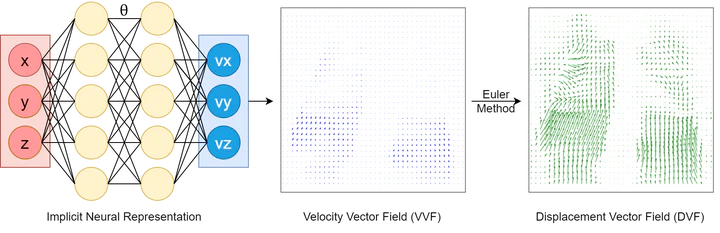 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: UnsplashAbstract
Background and purpose: Deformable image registration (DIR) is a crucial tool in radiotherapy for extracting and modelling organ motion. However, when significant changes and sliding boundaries are present, it faces compromised accuracy and uncertainty, determining the subsequential contour propagation and dose accumulation procedures. Materials and methods: We propose an implicit neural representation (INR)-based approach modelling motion continuously in both space and time, named Continues-sPatial-Temporal DIR (CPT-DIR). This method uses a multilayer perception (MLP) network to map 3D coordinate (x,y,z) to its corresponding velocity vector (vx,vy,vz). The displacement vectors (dx,dy,dz) are then calculated by integrating velocity vectors over time. The MLP’s parameters can rapidly adapt to new cases without pre-training, enhancing optimisation. The DIR’s performance was tested on the DIR-Lab dataset of 10 lung 4DCT cases, using metrics of landmark accuracy (TRE), contour conformity (Dice) and image similarity (MAE).
Add the publication’s full text or supplementary notes here. You can use rich formatting such as including code, math, and images.